PTFE, or polytetrafluoroethylene, is a synthetic fluoropolymer that has become a popular material in a wide range of industries due to its unique properties, such as high chemical resistance, non-stick surface, and low coefficient of friction. Modified PTFE, also known as MPTFE and TFM, is a chemically modified version of PTFE that offers higher performance.
In this blog post, we will explore what modified PTFE is, its benefits, the regular grades available, and how to find a reliable supplier.
What Is Modified PTFE?
Modified PTFE can be considered a second-generation PTFE. It is a tetrafluoroethylene-based copolymer that incorporates a small amount (less than 1%) of perfluorinated modifier (PPVE) into its molecular structure. It’s greatly improved on the performance of standard PTFE, which has a higher permeation resistance, lower creep and smoother surface.
The modified chemical structure of the polymer allows us to distinguish between Standard PTFE and modified PTFE. The molecular weight of Modified PTFE is one-fifth that of Standard PTFE. This means that the PTFE particles fuse better, thus significantly contributing to a better weldability of components made of Modified PTFE.
The relatively low molecular weight of Modified PTFE would normally give rise to an end product with higher crystallinity and hence lower mechanical properties. However, the perfluoropropyl vinylether (PPVE) modifier in Modified PTFE specifically inhibits crystallization, thus increasing the amorphous content while maintaining the preferred mechanical properties of Standard PTFE. In addition, the modifier ensures better distribution of the crystallites in the amorphous matrix and dramatically reduces cold flow.
Benefits
Modified PTFE exhibits the typically positive properties of standard PTFE, such as excellent chemical resistance and thermal stability. Additionally, has the following advantages:
Substantially lower deformation under load
Part surfaces are smoother and less porous – components stay clean since they are less likely to trap contaminants
Longer flex life than PTFE
Improved weldability
Lower permeability
Higher transparency
Better compression stress relaxation, particularly at elevated temperatures
Highlights of the Modified PTFE properties advantage
Low Deformation under load
The cold flow or deformation under load of Modified PTFE is significantly lower than that of Standard PTFE. This applies both to unfilled Modified PTFE and Modified PTFE compounds.
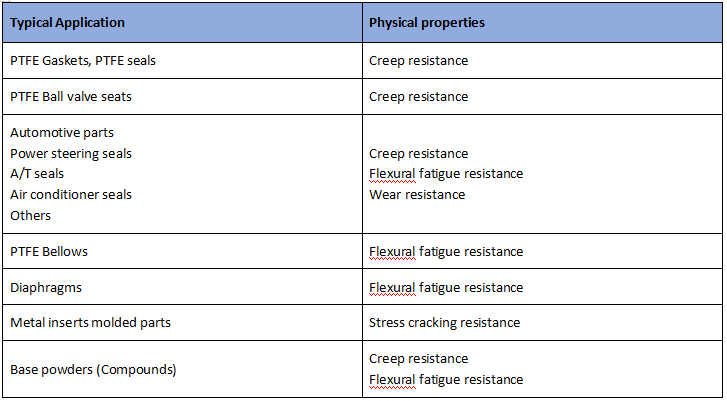
Flexural fatigue resistance
The modified PTFE has particularly good flexural fatigue resistance. Compared to standard PTFE, MIT tests show that modified PTFE has several times longer flexural life as that of standard PTFE. Even after the addition of inorganic fibers, the flexural fatigue resistance is better than that of standard PTFE. Because of this, modified PTFE can be used in dynamic applications which require a higher degree of reliability.
Reliability – especially at high temperatures.
Permanent total deformation after repeated loading of a test specimen, in each case measured at difference temperature.
For longer and smooth operation.
Stress recovery is important for applications such as seals, seats and gaskets where improved stress recovery can translate to longer seal-ability or less retorquing of parts. Modified PTFE exhibits better stress recovery than standard PTFE.
Applications
Modified PTFE is particularly suitable for use in applications where closed surfaces without pores are crucial. Products of modified PTFE with particularly smooth surfaces are of benefit when producing, transporting and storing ultra-pure chemicals, as well as in wet-chemical processes. The non-stick properties of modified PTFE make it resistant to adhesion by different substances, allowing for more efficient cleaning methods and shorter downtimes.
Chemical processing engineering
Fittings, shut-off devices, pumps, apparatus engineering
Semiconductor industry
Production, storage and transport of ultra-purity chemicals
Electronics industry
Machine and apparatus engineering
Vehicle construction and aerospace industry